The Netherlands
SNAPSHOT: Human spaceflight
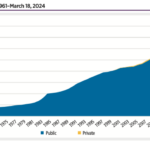
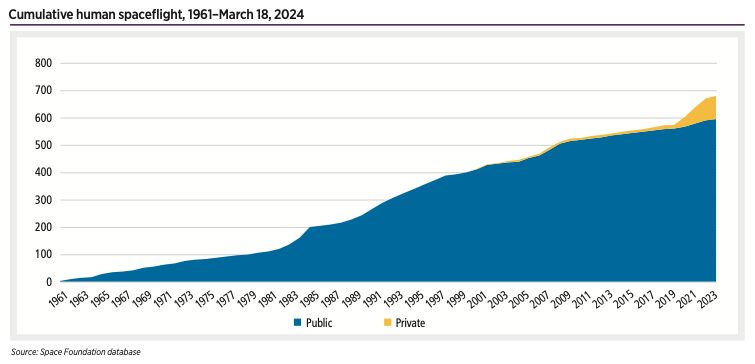
As of mid-March, 685 astronauts have reached at least 80 kilometers above the Earth’s surface. This total includes 86 private astronauts, 22 times as many as there were two decades ago.
2020 TSRQ3 – Infrastructure: Human Spaceflight


Since Yuri Gagarin’s orbital flight around the Earth in April 1961, humans in pioneering new technologies and pushing the limits of what’s considered possible. This year ushered in a new era of human spaceflight when SpaceX became the first . . .
2019 TSRQ3 – Education STEM Proficiency


The science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) workforce is at the core of the space industry—from the mathematicians and astronomers who analyze space to the engineers who design and build the launch vehicles that get us there. This workforce is enabled . . .
2019 TSRQ2 – Economy: Non-U.S. Government Space Investment

Growth in the government investment sector of the space economy outpaced commercial sectors as the U.S. and non-U.S. government shares of the global space economy between 2017 and 2018. . .
2016 – Matching Electric Vehicles to Charging Stations
Positioning, navigation, and timing technology comes together with databases, and socially-networked communications to pinpoint charging station availability.
European Space Industry Workforce by Country 2000 – 2020
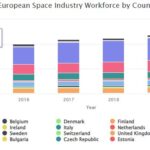
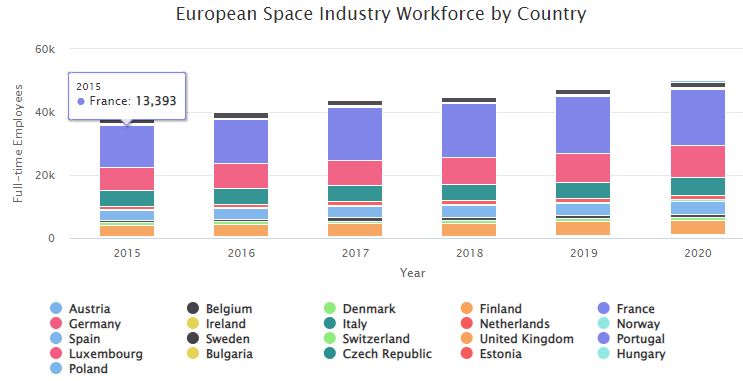
Stacked bar chart showing a twenty-year look at the European space industry workforce by country 2000 – 2020
2014 – Military Communications
Global, dedicated, and secure communications networks are vital to governments, militaries, and agencies around the world. Increased demand for capacity—particularly secure connectivity using non-commercial frequency bands—continued to drive deployment of dedicated military communications satellite systems. The U.S. military bought significant capacity from commercial operators such as Intelsat and SES in 2014. However, the way the military buys the bandwidth has been criticized by commercial satellite communications services as expensive and outdated.
2014 – Additional Country Space Budgets
Around the globe, many smaller nations—whether in terms of economy or population size—are investing in space projects or programs. The exhibit below shows the most recent available annual budget for civil space activities in a number of selected space states.
2013 – Military Communications
Dedicated and secure communications links are vital to defense agencies around the world. Increasing demand for capacity—particularly secure connectivity using non-commercial frequency bands—has driven the deployment of dedicated military communications satellites. The U.S. military buys a significant portion of its capacity from commercial operators such as Intelsat and SES. However, the United States also relies on military-specific systems such as the Wideband Global SATCOM (WGS) program, supplying dedicated communications to U.S. and allied military forces around the globe.
2013 – Galileo
A joint initiative between the European Commission (EC) and ESA, the Galileo constellation will consist of ## operational satellites in MEO. Europe launched ## in-orbit validation (IOV) spacecraft between 2011 and 2012 for positioning tests and technology validation. In November 2013, the IOV network enabled Galileo to successfully track a test aircraft flying over the Netherlands, the first time that the European agency has been able to track a moving aircraft using only the Galileo system. Initially, Galileo’s Open Service—freely accessibly PNT signals for mass-market devices such as smartphones and automobile navigation systems—is planned to be operational in 2014, although the launch of the first ## satellites has been delayed.