Australia
2019 TSRQ2 – Economy: Non-U.S. Government Space Investment

Growth in the government investment sector of the space economy outpaced commercial sectors as the U.S. and non-U.S. government shares of the global space economy between 2017 and 2018. . .
2017 – Communications Satellites – Snapshot
Aggregate revenues in the satellite communications industry have been relatively static over recent years, even as specific markets grew or declined. The 92 communications satellites deployed in…
2016 – Herding Cattle from Space
Ranchers and space technology work together to herd cattle.
2014 – Military Communications
Global, dedicated, and secure communications networks are vital to governments, militaries, and agencies around the world. Increased demand for capacity—particularly secure connectivity using non-commercial frequency bands—continued to drive deployment of dedicated military communications satellite systems. The U.S. military bought significant capacity from commercial operators such as Intelsat and SES in 2014. However, the way the military buys the bandwidth has been criticized by commercial satellite communications services as expensive and outdated.
The Train Network
Trains are using satellite technology—such as position, navigation, and timing (PNT) receivers and communications—to provide a train’s precise position to the people who manage European railway systems. While a train’s movements and schedule might be generally well-known, the PNT reporting will allow for a train’s precise position to be reported to a rail traffic control center, using a combination of 3G/4G data and satellite-based broadband services.
2014 – Additional Country Space Budgets
Around the globe, many smaller nations—whether in terms of economy or population size—are investing in space projects or programs. The exhibit below shows the most recent available annual budget for civil space activities in a number of selected space states.
2013 – Military Communications
Dedicated and secure communications links are vital to defense agencies around the world. Increasing demand for capacity—particularly secure connectivity using non-commercial frequency bands—has driven the deployment of dedicated military communications satellites. The U.S. military buys a significant portion of its capacity from commercial operators such as Intelsat and SES. However, the United States also relies on military-specific systems such as the Wideband Global SATCOM (WGS) program, supplying dedicated communications to U.S. and allied military forces around the globe.
2013 – Additional Country Space Budgets
Around the globe, many smaller nations—whether in terms of economy or population size—are investing in space projects or programs. Exhibit 2cc shows the most recent available yearly budget for civil space activities in a number of selected emerging space states. Each of these countries tends to feature a different focus in its space investment portfolio, so care must be taken in making generalizations.
2013 – Number of First-Degrees Awarded
The number of STEM first-degree (bachelor’s equivalent) graduates in many space-relevant countries has increased in recent years. The disciplines included here are physical, biological, and computer science; engineering; and mathematics.
2013 – TIMSS
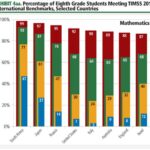
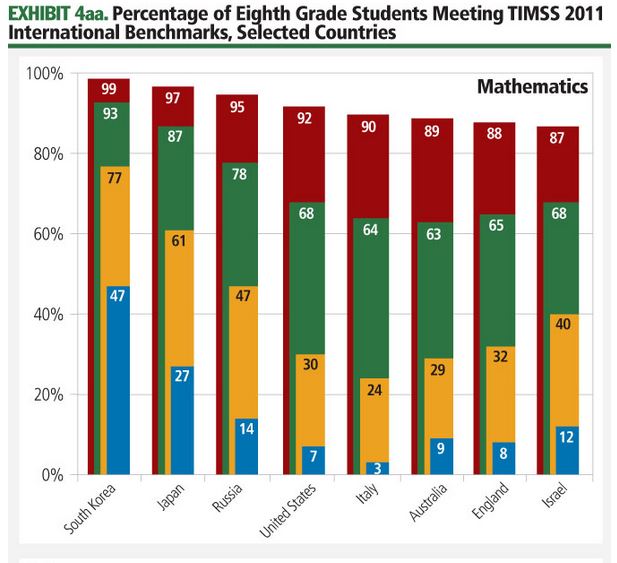
The TIMSS study also assesses mathematics and science knowledge and skills. Unlike PISA, which focuses on broader mathematical and scientific literacy of students nearing the end of compulsory education, TIMSS is designed to align broadly with the mathematics and science curricula in participating countries at the fourth and eighth grade (approximately 9- and 13-year-old) levels.